
Types of Earthing Systems TN, TT, IT and Earthing Systems
Contents
Nowadays, technical installations in all industries are characterized by ever-increasing complexity and automation. From highly developed production lines to robot technology, the amount of equipment that requires a reliable power supply to function smoothly is steadily growing. Therefore, the foundations for reliability and availability of an installation are already laid by selecting the right power supply system. Along with personnel and fire protection, fail safety is the key factor when choosing an appropriate power supply. During the planning phase of an installation, three system types are available: the TN system, the TT system and the IT system.
Protective measure always require the coordination of earth connection, types of conductive conductors and protective equipment in relation to the types of earthing systems. This clause describes the systems and their earth connection according to IEC 60364-1.
The standard assesses the following characteristics of the distribution system;
- Types of systems of live conductors;
- Types of system earthing.
Resulting from his are the following characteristic values for the type of distribution system
- Type and number of active conductors of the system
The systems are distinguished in AC and DC systems.
The following systems of live conductors are taken into account in the standard.
| AC System | DC System |
|---|---|
| Single-phase 2-wire | 2-wire |
| Single-phase 3-wire | 3-wire |
| Two-phase 3-wire | |
| Two-phase 5-wire | |
| Three-phase 3-wire | |
| Three-phase 3-wire |
Types of Systems Earthing
The various codes used, are derived from the relationship of the distribution system to earth and the relationship of the exposed conductive parts of the electrical installation to earth. Codes used have the following meaning;
| First letter | Relationship of distribution system to earth |
| T | Direct connection of one point to earth; |
| I | All live parts isolated from earth or one point connected to earth through an impedance |
| Second letter | Relationship of the exposed-conductive-parts of the installation to earth |
| T | Direct electrical connection of the exposed-conductive-parts to earthing independently of the earthing of any point of the power system; |
| N | Direct electrical connection of the exposed-conductive-parts to earthed point of the power system (in AC systems, the earthed point of the power system is normally the natural point or, if a neutral point is no available, a phase conductor). |
| Subsequent letter | Arrangement of neutral and protective conductors |
| S | Protective function provided by a conductor separate from the neutral of from the earthed line (or in AC systems, earthed phase) conductor. |
| C | Neutral and protective functions combined in a single conductor (PEN conductor) |
| PE | Protective conductor. |
The main distributor systems are;
TN System, TT System, IT System
TN System
TN Distributor systems have one point directly earthed, the exposed-conductive-parts of the installation being connected to that point by protective conductors. There are distinct types of TN Systems in relation to the arrangement of neutral and protective conductors. They are as follows;

- TN-S system: throughout the system, a separate protective conductor is used;
- TN-C-S system: neutral and protective functions are combined in a single conductor in a part of the system;
- TN-C system: neutral and protective functions are combined in a single conductor throughout the system.
TT System
The TT distributor system has one point directly earthed, the exposed conductive-parts of the installation being connected to earth electrodes electrically
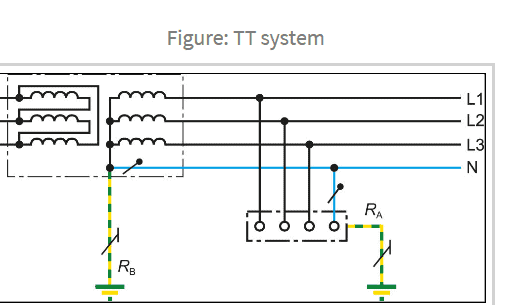
independent of the earth electrodes of the power system.
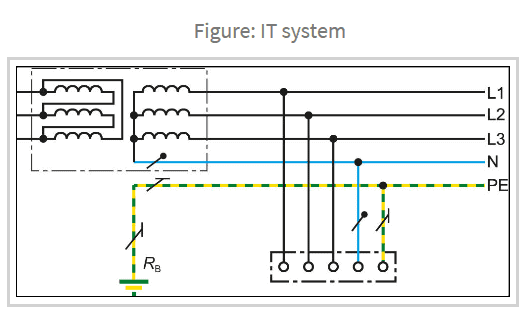
IT System
The IT distribution system has all live parts isolated from earth or one point connected to earth through an impedance, the exposed-conductive-parts of the electrical installation being earthed
- Independently, or
- Collectively, or
- To the earthing of the system
Result
Earthing systems are generally important to protect basic protection (against direct contact) and fault / fault protection (against indirect contact) against bumps and to minimize the risk of fire that can occur. Because the two important values we need to build protection and equip the circuits with the necessary protection devices depend on these systems. These two important values are the fault current and the touch voltage. Because the protection will change by the size of these values. These values depend entirely on what the earthing system is.
References
- W. Hofheinz: Fault Current Monitoring in Electrical Installations
- Aktif Muhendislik Medical Power Systems Catalogue
Harun Öndül
Sales Manager
Aktif Mühendislik



eren One Comment
sengi semu
says:good and so eraborative work